Artificial intelligence is moving beyond recommendations and automation into a new frontier where AI agents can independently initiate and complete financial transactions. This evolution, known as agentic payments technology, represents a fundamental shift in how money moves through the digital economy. As businesses navigate AI automations going into 2026 and beyond, understanding agentic payments technology is essential for remaining competitive in an increasingly AI-driven marketplace.
In this guide, you’ll discover:
- What agentic payments technology is, and how it differs from traditional payment automation
- The two major protocols shaping the future of AI-driven transactions
- Real-world use cases across industries, from retail to B2B finance
- Security considerations and trust barriers affecting adoption
- How agentic payments enable the next generation of commerce
What Is Agentic Payments Technology?
Agentic payments technology refers to payment systems where artificial intelligence agents can autonomously make purchasing decisions and execute transactions without direct human intervention at the moment of payment. Unlike traditional autopay systems that simply follow preset schedules, agentic AI evaluates real-time conditions, analyzes data from multiple sources, and determines the optimal timing, amount, and method for each payment.
The distinction is significant. Traditional payment automation operates on fixed rules: pay this amount on this date. Agentic payments technology introduces reasoning, learning, and adaptive decision-making into the process. An AI agent might analyze inventory levels, supplier pricing, market conditions, and cash flow projections before executing a purchase order payment, adjusting terms based on real-time data – all in a goal-driven manner.
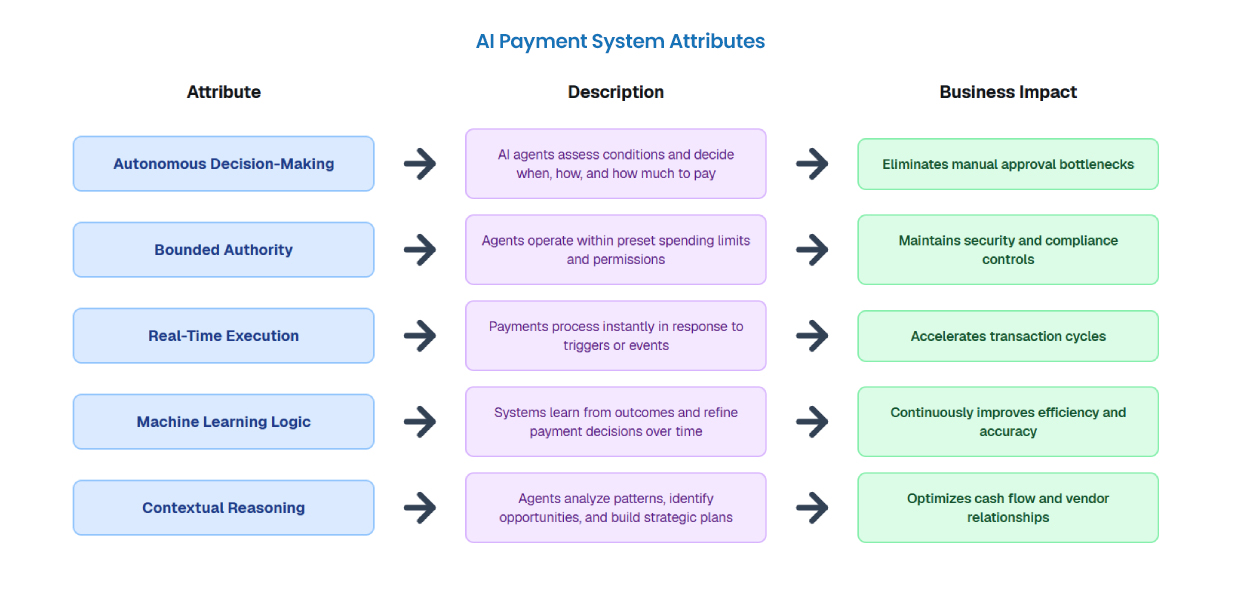
This autonomous capability is powered by several core attributes:
What Makes Agentic Payments So Impactful for Businesses
The payments industry, which handles more than $26 trillion in annual transactions globally, recognizes that agentic payments technology addresses long-standing inefficiencies in payment processing while creating new capabilities for customer service and operational excellence.
How Agentic Payments Technology Works
Agentic payments technology operates through a structured process that combines AI decision-making with secure financial execution. Understanding this workflow is essential for businesses evaluating implementation strategies.
1. Agent Configuration
Organizations first create AI agents with specific financial objectives, such as managing subscription renewals, paying vendor invoices, or executing procurement orders. Each agent connects to a payment source, such as a corporate bank account, digital wallet, or cryptocurrency wallet, and operates within clearly defined boundaries and spending limits established by the business.
2. Continuous Monitoring
Once deployed, the AI agent continuously monitors relevant data streams and environmental signals. This might include account balances, contract terms, pricing fluctuations, inventory levels, or market conditions. The agent integrates with enterprise systems like ERP platforms, accounting software, and external APIs to collect real-time information that informs payment decisions. Monitoring will also involve autonomous checks related to fraudulent and/or incorrect transactions.
3. Intelligent Decision-Making
The agent then evaluates whether conditions warrant a payment. Some agentic payments technology uses rule-based logic (if X condition is met, execute Y payment), while more sophisticated systems employ machine learning models that assess risk, optimize timing, and align actions with broader business objectives. This decision-making layer distinguishes agentic payments technology from simple automation.
4. Autonomous Execution
After determining that a payment should occur, the agent executes the transaction automatically through appropriate payment networks, such as credit cards, ACH transfers, real-time payment rails, or blockchain-based systems. The agent handles one-time, recurring, or multi-party payments and manages receipts, confirmations, and error resolution. This step will also involve any escalations for disputed based on the checks performed during monitoring.
5. Compliance and Auditability
Every action is logged with timestamps, data sources, decision rationale, and transaction outcomes. This creates a transparent audit trail for regulatory compliance, including KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks. Human oversight remains available for review, intervention, or policy adjustment as needed.
This five-step framework transforms payments from manual tasks into dynamic, self-regulating processes that operate 24/7 across global time zones.
Major Agentic Payments Technology Protocols
The agentic payments technology landscape is being defined by two primary protocols, each backed by major industry players and designed to enable secure, scalable AI-driven transactions.
OpenAI’s Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP)
Developed in partnership with Stripe, the Agentic Commerce Protocol is an open-standard framework that enables secure, frictionless transactions inside conversational platforms like ChatGPT. ACP transforms chat interfaces into commerce channels, allowing users to browse, compare, and purchase products without leaving the conversation.
The protocol uses shared payment tokens to facilitate secure transactions. When a customer confirms a purchase through an AI agent, the system creates a time-limited, usage-controlled token that authorizes payment without exposing sensitive credentials. Businesses maintain their role as the merchant of record and use their existing payment service providers, ensuring transactions flow through established infrastructure.
ACP currently powers “Instant Checkout” in ChatGPT, where US users can purchase directly from Etsy sellers. Shopify merchants, including major brands, will be coming soon. The protocol supports physical and digital goods, subscriptions, and asynchronous purchases, making it a scalable foundation for agentic commerce.
Google’s Agent Payments Protocol (AP2)
Google’s Agent Payments Protocol takes a different approach, prioritizing trust, verification, and interoperability across global payment networks. More than 60 organizations, including Mastercard, American Express, PayPal, Adyen, and Coinbase, are collaborating to bring AP2 to production.
AP2 uses cryptographically signed mandates, which are tamper-proof digital contracts that define exactly what an agent can do on a customer’s behalf. For example, a mandate might specify: “Book a vacation package to Los Cabos under $2,000, only through these five travel partners, within the next three months.” Once authorized by the customer, the agent executes transactions according to these parameters, creating a full audit trail that documents permitted actions.
The protocol supports two primary interaction types:
- Real-time purchases where customers approve each transaction after the agent presents options
- Delegated tasks where agents operate autonomously within pre-approved parameters for recurring purchases
Below is a rundown of how ACP and AP2 differ in the way they handle different agentic payment features:
| Feature | ACP (OpenAI + Stripe) | AP2 (Google + Partners) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Type | Open, community-driven (Apache 2.0) | Open, enterprise-grade framework |
| Payment Methods | Card, bank, ACP-compatible PSPs | Card, bank transfer, crypto, stablecoins |
| Authorization Model | Shared payment tokens | Cryptographically signed mandates |
| Launch Partners | Stripe, Shopify, Etsy | Mastercard, AmEx, PayPal, Coinbase |
| Primary Use Cases | Conversational commerce, instant checkout | Cross-platform transactions, Web3 integration |
| Compliance Focus | Secure tokenization, audit trails | Strong cryptographic verification, regulatory alignment |
Enterprises may need to integrate both protocols as the ecosystem matures. Interoperability between ACP and AP2 will become increasingly important as more merchants and financial institutions adopt agentic payments technology.
Agentic Payments Technology Use Cases
Agentic payments technology is already demonstrating value across multiple industries and business functions. These real-world applications illustrate how autonomous AI agents are transforming financial operations:
Consumer Finance Management
Personal AI finance agents now extend beyond bill reminders to actively manage household finances. These agents can make purchases when conditions are optimal, pay bills when funds are available, cancel unused subscriptions automatically, and move money between savings and investment accounts based on cash flow analysis. This level of autonomous financial management frees consumers from routine money management tasks.
Enterprise Accounts Payable
For businesses, agentic payments technology reduces manual work in finance and accounting operations. AI agents can approve invoices against purchase orders, trigger payments upon delivery confirmation, reconcile transactions across multiple systems, and optimize working capital by moving funds between accounts. Processing a single invoice manually costs around $13 on average, making automation through agentic payments technology a significant cost-reduction opportunity.
IoT and Connected Devices
The Internet of Things creates new payment scenarios where devices transact with each other. A manufacturing robot might automatically order replacement parts when diagnostics indicate upcoming maintenance needs. An electric vehicle could pay for charging at any station without driver intervention. Smart home systems might purchase utilities or services based on usage patterns and rate optimization.
B2B Procurement and Supply Chain
In business-to-business contexts, agentic payments technology enables sophisticated procurement workflows. A supplier’s invoice-to-cash agent can generate invoices and negotiate with a buyer’s procure-to-pay agent, potentially arranging working capital financing or invoice discounting when market conditions warrant. These agent-to-agent interactions streamline complex business processes.
Subscription and Recurring Revenue Management
Software-as-a-service companies and subscription businesses can use agentic payments technology to optimize recurring revenue. AI agents can manage subscription renewals, process upgrades or downgrades based on usage patterns, handle failed payment recovery, and implement dynamic pricing strategies in real-time.
Security Challenges and Trust Barriers
Despite the promise of agentic payments technology, significant obstacles remain before widespread adoption. Understanding these challenges is essential for businesses planning implementation strategies.
The Trust Deficit
Consumer trust in AI-powered financial services remains limited. Recent surveys indicate that only 29% of UK consumers would trust AI to make small, automated payments on their behalf, while US adoption stands at just 16%. This skepticism extends to institutional confidence, where banks express concerns about unauthorized transactions, compromised agent credentials, and potential multi-agent attacks.
According to research from Accenture, 87% of executives believe that trust will be the most significant barrier to agentic payments technology adoption. This trust gap reflects broader concerns about AI decision-making in high-stakes financial contexts where errors have immediate consequences.
Key regulatory questions include:
- Who bears liability when an AI agent makes an unauthorized transaction?
- How do existing KYC and AML regulations apply to AI agents?
- What disclosure requirements apply to agent-initiated payments?
- How should regulators classify and oversee agent-to-agent transactions?
Global non-compliance costs reached $14 billion in 2024, with AML fines alone exceeding $6 billion. This sobering context explains institutional caution around deploying autonomous agents that could potentially amplify compliance risks.
Fraud Detection Complexity
Agentic payments technology introduces new fraud vectors that traditional security systems aren’t designed to address. Financial institutions must develop new approaches for:
- Distinguishing legitimate agents from malicious bots
- Detecting compromised agent credentials
- Identifying insider threats using rogue agents
- Preventing first-party fraud where users claim agents acted without authorization
Industry analysts estimate AI-enabled fraud accounted for approximately 20% of all fraud in 2024, and this percentage is expected to increase as agentic systems become more prevalent.
Agentic Payments Technology as the Foundation for Agentic Commerce
Agentic payments technology is not an isolated innovation; it serves as the critical infrastructure enabling a broader transformation called agentic commerce, where AI agents manage the entire shopping journey from discovery through checkout.
In agentic commerce, consumers delegate purchasing decisions to AI agents that understand their preferences, budget constraints, and buying patterns. When a user says, “I need new running shoes under $150,” the agent searches across multiple retailers, compares options based on the user’s past purchases and reviews, identifies the best value proposition, and completes the purchase autonomously. This is all made possible by agentic payments technology.
McKinsey research projects that by 2030, agentic commerce could generate between $3 trillion and $5 trillion globally, including up to $1 trillion in the US B2C retail market alone. This massive opportunity depends entirely on secure, scalable agentic payments technology that can handle billions of autonomous transactions.
The timeline for widespread adoption is accelerating. Industry research indicates that 57% of executives believe agentic payments technology will become mainstream within the next three years. However, truly autonomous, end-to-end systems where agents initiate, authorize, and settle complex transactions without human oversight are projected to materialize within 3-7 years, with initial, highly controlled rollouts occurring sooner. This timeline reflects the need for absolute reliability, robust regulatory frameworks, and paramount security.
Preparing for an Agentic Future
The rise of agentic payments technology represents a defining moment for businesses across industries. Organizations that understand and adapt to this shift will position themselves at the forefront of Digital Transformation, while those that hesitate risk being left behind as AI agents increasingly mediate commercial transactions.
At 7T, we’re guided by our philosophy of “Business First, Technology Follows.” As such, the 7T development team works with company leaders who are seeking to solve problems and drive ROI through Digital Transformation and innovative technologies like AI. We understand that implementing agentic payments technology requires more than technical expertise—it demands a strategic approach that aligns AI capabilities with business objectives, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations.
7T has offices in Dallas and Houston, but our clientele spans the globe. If you’re ready to discuss your Digital Transformation project and explore how agentic payments technology can transform your business operations, contact 7T today.